A Guide to Choosing the Right Tools for Phlebotomy Practice
Are you an aspiring or experienced phlebotomist looking to enhance your skills and efficiency in blood collection procedures? One of the key factors that contribute to a successful phlebotomy practice is having the right tools at your disposal. The choice of tools can significantly impact patient comfort, the accuracy of blood collection, and the overall quality of your work. In this guide, we’ll delve into the essential tools for phlebotomy practice, offering valuable insights to help you make informed decisions.
Needle Gauges: Finding the Perfect Fit
Selecting the appropriate needle gauge is crucial for a smooth and comfortable blood collection experience. Needle gauge refers to the thickness of the needle, with smaller numbers indicating thicker needles. The choice of gauge depends on the purpose of the blood draw and the patient’s vein condition.
For routine venipuncture, commonly used needle gauges range from 20 to 22. Thinner needles (23-25 gauge) are preferred for delicate veins, such as those of pediatric and elderly patients. Thicker needles (18-19 gauge) are typically employed for procedures involving blood donation or patients with difficult-to-access veins.
Remember, the goal is to minimize patient discomfort while ensuring successful blood collection. Always assess the patient’s veins and condition before selecting a needle gauge and be prepared to adjust your choice based on the specific circumstances.
Tourniquets: Balancing Pressure and Comfort
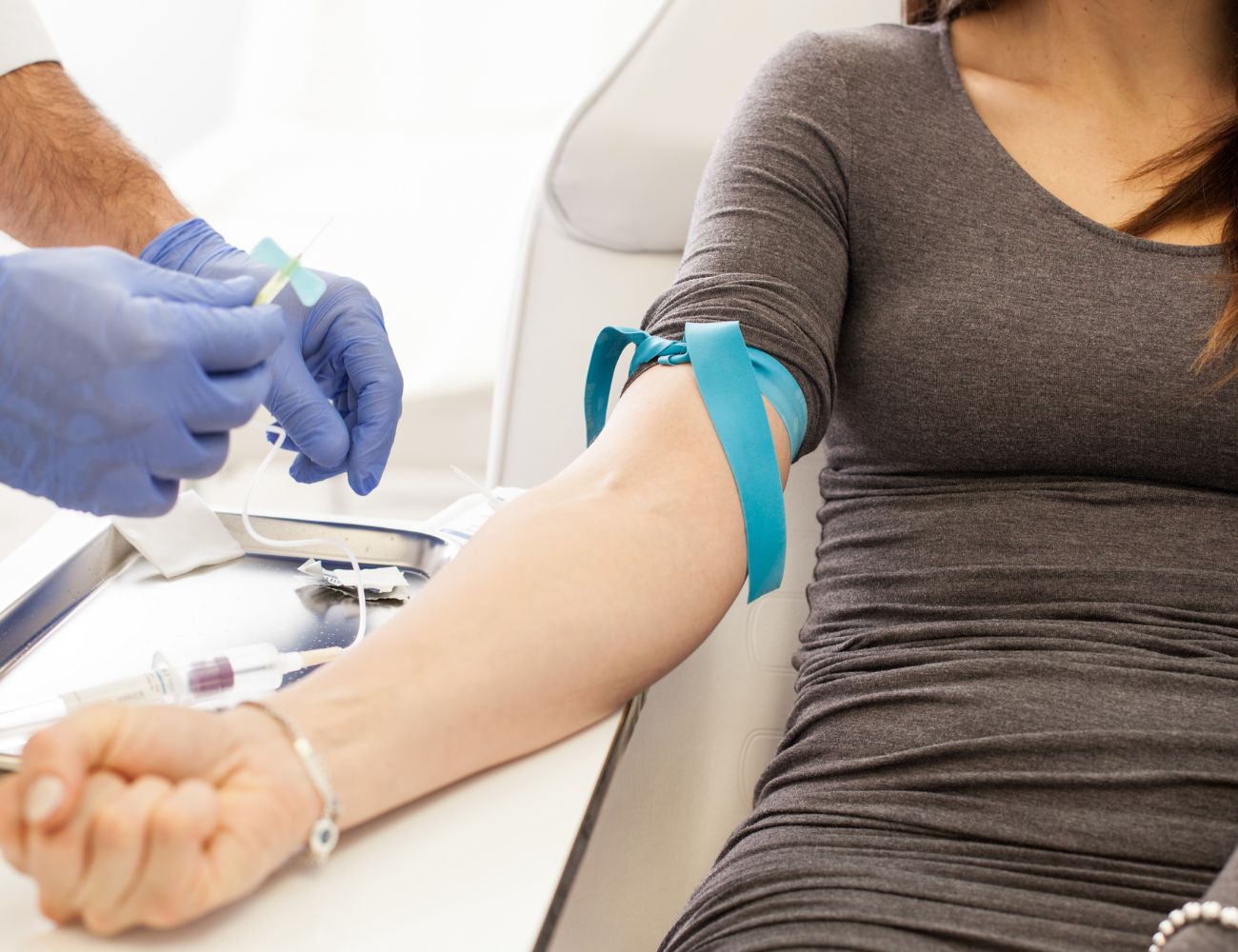
Tourniquets are essential for engorging veins and making them more visible and accessible. While applying the tourniquet, striking a balance between sufficient pressure and patient comfort is vital. Tourniquets that are too tight can cause discomfort and potentially affect blood test results, while those that are too loose may not aid in vein dilation.
Opt for tourniquets made from durable, latex-free materials that are easy to clean and sanitize. Adjustable tourniquets provide flexibility in achieving the right amount of pressure. It’s also a good practice to inform patients about the tourniquet’s purpose and reassure them that it will be released as soon as the vein is accessed.
Blood Collection Sets: Simplifying the Procedure
Blood collection sets, commonly known as needle and tubing sets or “butterfly” needles, offer enhanced maneuverability during blood draws. They are particularly useful for patients with small or fragile veins, where maintaining needle stability is a challenge. These sets come in various sizes, allowing you to choose the one that best suits your patient’s needs.
When selecting a blood collection set, prioritize safety features like safety needles with retractable mechanisms to prevent accidental needlestick injuries. Additionally, opt for sets with color-coded adapters that help ensure the right tubes are used for specific tests.
Gloves: Ensuring Hygiene and Safety
Gloves are a fundamental tool that promotes both patient and phlebotomist safety. They protect you from potential bloodborne pathogens while also ensuring patient hygiene. Latex-free gloves are recommended to prevent allergic reactions and comply with modern healthcare standards.
When choosing gloves, prioritize a comfortable fit that allows for dexterity during the blood collection process. Consider using nitrile gloves, which provide a strong barrier while offering tactile sensitivity.
Tubes and Containers: Accurate Sample Collection
Accurate sample collection is the cornerstone of successful phlebotomy practice. The choice of tubes and containers plays a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity of blood samples for various tests.
Different tubes are designed to collect different types of samples, such as serum, plasma, or whole blood. Make sure you’re well-versed in the color-coding system used for tubes, as this indicates the type of additive present and the tests for which they’re suitable.
Staying organized with clearly labeled tubes and containers prevents cross-contamination and ensures that samples are properly identified.
Alcohol Swabs and Antiseptics: Prioritizing Aseptic Technique
Maintaining aseptic technique is crucial for preventing infections and ensuring patient safety. Alcohol swabs and antiseptics are used to clean the site of venipuncture, reducing the risk of introducing pathogens into the bloodstream.
Choose alcohol swabs that contain at least 70% isopropyl alcohol, as this concentration is effective at disinfecting the skin. Use a circular motion to clean the area and allow it to air dry before performing the blood draw.
In Conclusion
Phlebotomy stands as a critical pillar within healthcare, with the choice of tools significantly impacting patient experiences and the precision of test outcomes. Equipping yourself with optimal instruments is your responsibility as a phlebotomist. Embrace patient well-being, safety, and precise sample collection as you make selections. Stay updated on evolving tools and techniques to remain at the forefront, delivering exceptional patient care. By mastering needle gauges, tourniquets, blood collection sets, gloves, tubes, and antiseptics, you’ll be primed to thrive in your phlebotomy journey. Adapt your tool preferences to suit each unique patient, and blend the right tools with expert techniques for a rewarding and successful career in phlebotomy.